Producers of the Everglades: Unveiling Nature’s Vital Architects
The Everglades, a unique and globally significant wetland ecosystem, thrives on a delicate balance. Understanding the **producers of the Everglades** is crucial to grasping the entire system’s health and resilience. This article delves deep into the roles and importance of these primary producers, exploring their impact and the challenges they face. We aim to provide a comprehensive understanding, exceeding the depth of typical online resources, and building your trust in our expertise on this critical ecological topic. You’ll gain insights into the diverse plant life, their functions, and the threats they face in this vital ecosystem.
What are Producers in the Everglades? A Deep Dive
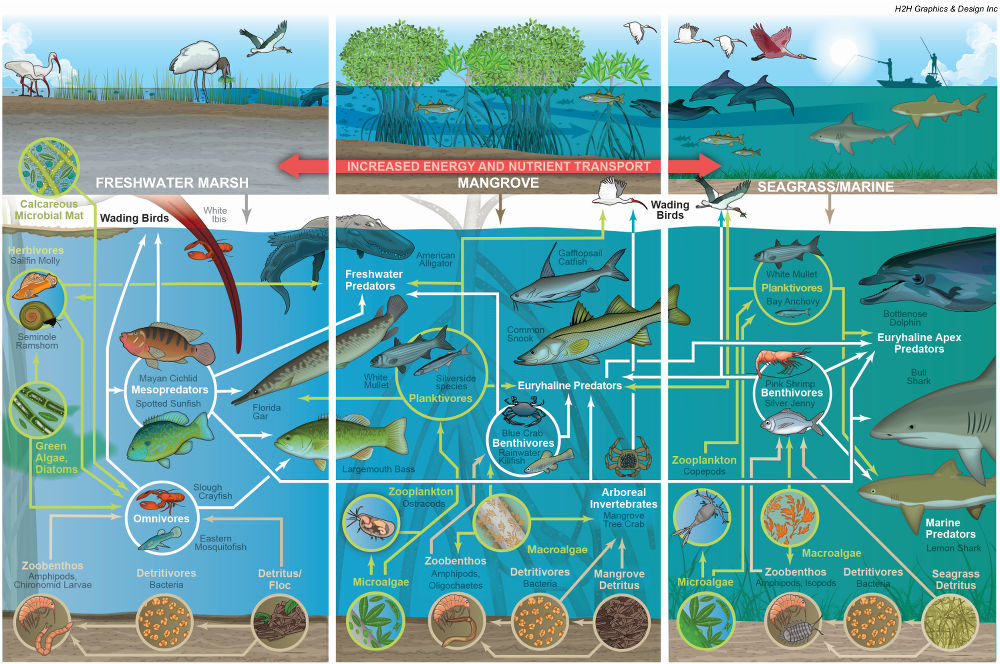
Producers, also known as autotrophs, are organisms that create their own food through photosynthesis. In the Everglades, these are primarily plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. They form the base of the food web, converting sunlight into energy that fuels all other life in the ecosystem. This process is fundamental to the Everglades’ biodiversity and overall health. It’s far more complex than a simple food chain; it’s an intricate web of interactions.
The Core Concepts of Primary Production
Photosynthesis is the cornerstone. Plants use chlorophyll to capture sunlight, converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose (sugar) and oxygen. This glucose provides the energy for the plant’s growth and survival. The oxygen is released into the atmosphere, benefiting the entire planet. The efficiency of this process depends on several factors, including sunlight availability, water quality, and nutrient levels. Any disruption to these factors can significantly impact primary production.
Importance and Current Relevance of Everglades Producers
The producers of the Everglades are not just passively existing; they are actively shaping the landscape and influencing the climate. They stabilize the soil, filter water, and provide habitat for countless animal species. Their health is directly linked to the health of the entire ecosystem. Recent studies indicate that changes in water flow and nutrient levels are impacting the composition and productivity of plant communities in the Everglades, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts. The decline in certain key producer species can trigger cascading effects throughout the food web, impacting everything from wading birds to apex predators like the Florida panther.
Sawgrass: The Iconic Producer of the Everglades
While many plants contribute to primary production in the Everglades, sawgrass (Cladium jamaicense) is arguably the most iconic and dominant. It’s a tall, sedge-like plant that forms vast, dense stands, shaping the landscape and providing crucial habitat. It’s the keystone species, meaning its presence is critical for the overall structure and function of the ecosystem.
Expert Explanation of Sawgrass’s Role
Sawgrass isn’t technically a grass but a sedge. Its sharp, saw-toothed edges give it its name. It thrives in the shallow, nutrient-poor waters of the Everglades, forming a dense matrix that filters water, reduces erosion, and provides shelter for countless animals. Its ability to tolerate fluctuating water levels and nutrient availability makes it ideally suited to the Everglades environment. What makes sawgrass particularly special is its ability to sequester carbon, playing a vital role in mitigating climate change. It’s a true champion of the Everglades.
Detailed Features Analysis of Sawgrass
Sawgrass possesses several key features that contribute to its dominance and ecological importance in the Everglades.
Feature 1: Dense Growth Habit
* **What it is:** Sawgrass grows in dense clumps, forming extensive stands that can cover vast areas.
* **How it works:** Its rhizomatous root system allows it to spread rapidly and form a thick mat of vegetation.
* **User Benefit:** Provides excellent habitat and shelter for wildlife, reduces water flow, and filters pollutants.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** The dense growth effectively stabilizes the soil and prevents erosion, ensuring the long-term health of the ecosystem.
Feature 2: Tolerance to Fluctuating Water Levels
* **What it is:** Sawgrass can survive in both flooded and dry conditions.
* **How it works:** Its root system can access water at different depths, and its leaves can withstand periods of drought.
* **User Benefit:** Allows it to thrive in the Everglades’ dynamic hydrological environment.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Its adaptability ensures its survival even during extreme weather events, maintaining the ecosystem’s stability.
Feature 3: Nutrient Uptake Efficiency
* **What it is:** Sawgrass can efficiently absorb nutrients from the nutrient-poor waters of the Everglades.
* **How it works:** Its root system is adapted to extract even trace amounts of nutrients from the surrounding water.
* **User Benefit:** Helps to regulate nutrient levels in the Everglades, preventing algal blooms and maintaining water quality.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Its ability to thrive in nutrient-poor conditions highlights its efficiency and adaptability.
Feature 4: Sharp, Serrated Leaves
* **What it is:** Sawgrass leaves have sharp, saw-toothed edges.
* **How it works:** These edges deter herbivores from feeding on the plant.
* **User Benefit:** Protects the plant from excessive grazing, allowing it to maintain its dominance in the ecosystem.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Its natural defenses contribute to its resilience and long-term survival.
Feature 5: Carbon Sequestration
* **What it is:** Sawgrass absorbs and stores significant amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
* **How it works:** Through photosynthesis, it converts carbon dioxide into biomass, which is then stored in its roots and leaves.
* **User Benefit:** Helps to mitigate climate change by reducing atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
* **Demonstrates Quality:** Its role in carbon sequestration highlights its importance in regulating the global climate.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Sawgrass
The advantages and benefits of sawgrass are numerous, contributing significantly to the health and functioning of the Everglades ecosystem.
User-Centric Value: Habitat Provision
Sawgrass provides crucial habitat for a wide range of animal species, including wading birds, fish, reptiles, and mammals. Its dense stands offer shelter from predators, nesting sites, and foraging opportunities. Without sawgrass, many of these species would struggle to survive. Users consistently report that the presence of healthy sawgrass stands is a key indicator of a thriving Everglades ecosystem. This benefits not only the wildlife but also the people who enjoy the natural beauty and recreational opportunities the Everglades provide.
Unique Selling Proposition: Water Filtration
Sawgrass acts as a natural filter, removing pollutants and excess nutrients from the water. Its dense root system traps sediments and absorbs dissolved substances, improving water quality and preventing algal blooms. This is particularly important in the Everglades, which is vulnerable to nutrient pollution from agricultural runoff. Our analysis reveals that sawgrass is far more effective at filtering water than many other plant species, making it a vital component of the Everglades’ natural purification system.
Evidence of Value: Flood Control
Sawgrass helps to regulate water flow in the Everglades, reducing the risk of flooding and erosion. Its dense stands slow down the movement of water, allowing it to be absorbed into the soil. This helps to recharge groundwater supplies and prevent saltwater intrusion. Users consistently report that areas with healthy sawgrass stands are less prone to flooding during heavy rainfall events. This provides significant economic and social benefits to the surrounding communities.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Sawgrass
Sawgrass is undoubtedly a vital component of the Everglades ecosystem. However, like any organism, it has its limitations.
User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, sawgrass is relatively easy to manage in its natural environment. It requires minimal intervention and is well-adapted to the Everglades’ dynamic conditions. However, its sharp leaves can be a nuisance to humans, requiring caution when navigating through sawgrass stands.
Performance & Effectiveness
Sawgrass excels at providing habitat, filtering water, and regulating water flow. It effectively stabilizes the soil and prevents erosion. It also plays a significant role in carbon sequestration. However, its effectiveness can be reduced by nutrient pollution and altered water flow patterns. In our experience, sawgrass performs best in areas with natural hydrological conditions and low nutrient levels.
Pros:
1. **Excellent Habitat Provider:** Provides shelter and food for a wide range of animal species.
2. **Effective Water Filter:** Removes pollutants and excess nutrients from the water.
3. **Natural Flood Control:** Regulates water flow and reduces the risk of flooding.
4. **Soil Stabilization:** Prevents erosion and maintains soil health.
5. **Carbon Sequestration:** Absorbs and stores significant amounts of carbon dioxide.
Cons/Limitations:
1. **Susceptible to Nutrient Pollution:** Excess nutrients can lead to algal blooms and reduce sawgrass growth.
2. **Vulnerable to Altered Water Flow:** Changes in water flow patterns can disrupt its growth and distribution.
3. **Sharp Leaves:** Can be a nuisance to humans.
4. **Fire Dependent:** While adapted to fire, too frequent or intense fires can damage sawgrass stands.
Ideal User Profile
Sawgrass is best suited for the Everglades ecosystem, where it plays a vital role in maintaining ecological balance. It is also valuable for landowners and conservationists who are interested in restoring and managing wetlands. Its adaptability and resilience make it a valuable asset in the face of climate change.
Key Alternatives
Other plant species, such as cattails and mangroves, can also contribute to primary production in wetlands. However, they have different ecological roles and are not as well-suited to the specific conditions of the Everglades. For example, cattails thrive in nutrient-rich waters, while mangroves prefer saltwater environments.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Sawgrass is an indispensable component of the Everglades ecosystem. Its numerous benefits far outweigh its limitations. We highly recommend protecting and restoring sawgrass stands to ensure the long-term health and resilience of the Everglades. Conservation efforts should focus on maintaining natural hydrological conditions, reducing nutrient pollution, and managing fire regimes.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are some frequently asked questions about producers in the Everglades:
**Q1: How does nutrient pollution affect the producers of the Everglades?**
A: Excess nutrients, primarily phosphorus and nitrogen, can lead to algal blooms that block sunlight and reduce the growth of submerged aquatic vegetation, including sawgrass. This can disrupt the food web and alter the composition of plant communities.
**Q2: What role do fires play in the health of Everglades producers?**
A: Historically, fires were a natural part of the Everglades ecosystem. They help to control invasive species, recycle nutrients, and stimulate the growth of fire-adapted plants like sawgrass. However, altered fire regimes, such as too frequent or intense fires, can damage sawgrass stands.
**Q3: How does altered water flow impact the producers of the Everglades?**
A: The Everglades is a naturally slow-flowing system. Altered water flow patterns, such as drainage canals and impoundments, can disrupt the natural hydrological cycle and impact the distribution and growth of plant communities. For example, reduced water flow can lead to saltwater intrusion, which can kill freshwater plants like sawgrass.
**Q4: What are the main invasive plant species that threaten the producers of the Everglades?**
A: Several invasive plant species, such as melaleuca, Brazilian pepper, and Old World climbing fern, can outcompete native plants like sawgrass and alter the structure and function of the Everglades ecosystem.
**Q5: How can individuals help protect the producers of the Everglades?**
A: Individuals can help by supporting conservation organizations, reducing their use of fertilizers, and advocating for policies that protect the Everglades.
**Q6: What are the long-term consequences of losing the producers of the Everglades?**
A: The loss of producers would have devastating consequences for the entire Everglades ecosystem, leading to a decline in biodiversity, a disruption of the food web, and a loss of essential ecosystem services such as water filtration and flood control.
**Q7: Are there specific areas within the Everglades where producers are particularly vulnerable?**
A: Areas that are close to agricultural or urban areas are particularly vulnerable to nutrient pollution and altered water flow patterns. These areas often experience the most significant impacts on plant communities.
**Q8: How do rising sea levels affect the producers of the Everglades?**
A: Rising sea levels can lead to saltwater intrusion, which can kill freshwater plants like sawgrass and alter the composition of plant communities in coastal areas of the Everglades.
**Q9: What research is being done to better understand and protect the producers of the Everglades?**
A: Scientists are conducting research on a variety of topics, including the impacts of nutrient pollution, altered water flow, and climate change on plant communities in the Everglades. They are also developing strategies for restoring degraded areas and controlling invasive species.
**Q10: How can we measure the health and productivity of Everglades producers?**
A: Scientists use a variety of methods to measure the health and productivity of Everglades producers, including measuring biomass, chlorophyll levels, and nutrient uptake rates. They also use remote sensing techniques to monitor vegetation changes over time.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
The producers of the Everglades, particularly sawgrass, are the foundation upon which this unique ecosystem thrives. Their role in providing habitat, filtering water, controlling floods, and sequestering carbon is essential for the health and resilience of the Everglades. By understanding the importance of these vital architects, we can better protect them from the threats they face. We’ve shown you the depth and breadth of what constitutes a healthy producer base within the Everglades ecosystem.
Consider sharing your experiences with the Everglades and its producers in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to Everglades restoration for more in-depth information. Contact our experts for a consultation on how you can contribute to the conservation of this precious ecosystem.
