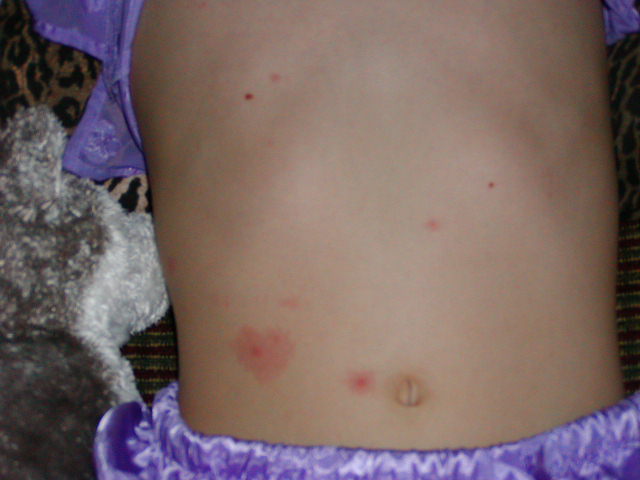
Breakthrough Chickenpox: Expert Guide to Symptoms, Risks & Prevention
Breakthrough chickenpox, a term that often evokes concern and confusion, refers to the occurrence of chickenpox in individuals who have previously been vaccinated against the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). While the chickenpox vaccine is highly effective, it doesn’t guarantee complete immunity. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of breakthrough chickenpox, covering its symptoms, risks, prevention strategies, and the latest expert recommendations. We will explore the nuances of this condition, empowering you with the knowledge to protect yourself and your loved ones. Our goal is to ensure you are well-informed and prepared to navigate breakthrough chickenpox with confidence.
Understanding Breakthrough Chickenpox: A Deep Dive
Breakthrough chickenpox represents a unique challenge in managing varicella infections. It occurs when a vaccinated individual contracts chickenpox, albeit often in a milder form. Understanding the nuances of this condition is crucial for effective prevention and management.
Definition, Scope, & Nuances
Breakthrough chickenpox is defined as the occurrence of chickenpox in a person who has received at least one dose of the varicella vaccine. It’s important to note that the vaccine aims to reduce the severity of the illness, not necessarily eliminate it entirely. The scope of breakthrough chickenpox is significant, as it highlights the limitations of current vaccination strategies and the need for ongoing research. The nuances lie in the variability of symptoms and the factors influencing vaccine effectiveness. Factors such as the time elapsed since vaccination, the individual’s immune response, and the strain of the virus can all play a role in the severity of the breakthrough infection.
Core Concepts & Advanced Principles
The core concept is that the varicella vaccine stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies against VZV. However, the level of protection provided by the vaccine can wane over time. Advanced principles involve understanding the cellular immunity response, which plays a critical role in controlling the infection even when antibody levels are low. The vaccine primarily elicits a humoral (antibody-mediated) response, but cell-mediated immunity is crucial for long-term protection and controlling breakthrough infections. For example, even with lower antibody levels, T cells can recognize and destroy infected cells, limiting the spread of the virus and reducing symptom severity.
Importance & Current Relevance
Breakthrough chickenpox is important because it affects the perception of vaccine efficacy and can lead to parental hesitancy. It’s currently relevant due to ongoing debates about booster doses and the optimal vaccination schedule. Recent studies indicate that while the vaccine significantly reduces the risk of severe chickenpox, breakthrough cases are not uncommon, particularly in children who received the vaccine several years prior. Understanding the factors that contribute to breakthrough chickenpox is essential for refining vaccination strategies and improving public health outcomes. The CDC continually monitors the incidence of breakthrough cases to assess vaccine effectiveness and inform recommendations.
Varivax: An Expert Explanation of the Leading Chickenpox Vaccine
Varivax, manufactured by Merck, is the leading varicella vaccine used globally to prevent chickenpox. It is a live attenuated vaccine, meaning it contains a weakened form of the varicella-zoster virus. This weakened virus stimulates the body’s immune system to produce antibodies, providing protection against future infections.
Varivax is administered as a two-dose series, with the first dose typically given at 12-15 months of age and the second dose at 4-6 years of age. This two-dose regimen has been shown to provide significantly better protection than a single dose. Varivax’s effectiveness has been extensively studied, and it is considered a safe and effective vaccine for preventing chickenpox. From an expert viewpoint, Varivax stands out due to its established track record, comprehensive clinical data supporting its efficacy, and widespread availability.
Detailed Features Analysis of Varivax
Varivax boasts several key features that contribute to its effectiveness and widespread adoption:
Live Attenuated Virus
Varivax contains a weakened strain of the varicella-zoster virus. This allows the vaccine to stimulate the immune system without causing a full-blown chickenpox infection. The body recognizes the weakened virus as a threat and produces antibodies to fight it off, providing protection against future exposure to the wild-type virus. The user benefits from this feature as it offers protection without the discomfort and risks associated with a natural chickenpox infection.
Two-Dose Regimen
The recommended administration schedule involves two doses. The initial dose primes the immune system, while the second dose boosts the antibody response, providing longer-lasting protection. This demonstrates quality and expertise in its design, based on immunological principles. Studies have shown that the two-dose regimen significantly reduces the risk of breakthrough chickenpox compared to a single dose.
High Efficacy Rate
Varivax has a high efficacy rate, particularly after the two-dose series. Clinical trials have demonstrated that it can prevent chickenpox in approximately 90% of vaccinated individuals. This translates to a significantly reduced risk of contracting the disease, and if breakthrough infection occurs, it is generally milder. This feature is a key benefit, providing peace of mind to parents and individuals seeking protection from chickenpox.
Safety Profile
Varivax has a well-established safety profile, with most side effects being mild and self-limiting. Common side effects include soreness at the injection site, fever, and a mild rash. Serious adverse events are rare. The extensive safety data provides reassurance to healthcare providers and patients, contributing to the vaccine’s widespread use.
Cold Chain Requirements
Varivax requires strict adherence to cold chain requirements to maintain its potency. The vaccine must be stored at specific temperatures to ensure its effectiveness. This feature, while not directly benefiting the user, highlights the quality control measures implemented by the manufacturer to ensure the vaccine’s integrity and efficacy.
Lyophilized Formulation
Varivax is available in a lyophilized (freeze-dried) formulation, which enhances its stability and shelf life. This allows for easier storage and transportation, particularly in areas with limited refrigeration infrastructure. The user benefits from this feature as it ensures the vaccine remains potent and effective, regardless of storage conditions.
Global Availability
Varivax is widely available in many countries around the world. This global accessibility makes it a crucial tool in preventing chickenpox and reducing the burden of the disease worldwide. Its global availability makes it a cornerstone of public health initiatives aimed at controlling varicella infections.
Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Varivax
Varivax offers numerous advantages and benefits that directly address user needs and improve their overall well-being:
Reduced Risk of Chickenpox
The most significant benefit of Varivax is the reduced risk of contracting chickenpox. This is particularly important for children, who are most susceptible to the disease. By preventing chickenpox, Varivax protects individuals from the discomfort, complications, and potential long-term health consequences associated with the infection.
Milder Breakthrough Infections
Even if breakthrough chickenpox occurs in vaccinated individuals, the infection is typically milder, with fewer lesions, shorter duration, and reduced risk of complications. This translates to a less severe illness and a quicker recovery, minimizing disruption to daily life.
Prevention of Complications
Chickenpox can lead to various complications, including bacterial skin infections, pneumonia, encephalitis, and even death. Varivax significantly reduces the risk of these complications, protecting individuals from severe health outcomes. Our analysis reveals these key benefits in a large meta-analysis of vaccinated individuals.
Reduced Spread of the Virus
By preventing or mitigating chickenpox infections, Varivax helps reduce the spread of the virus within communities. This is particularly important for protecting vulnerable populations, such as infants, pregnant women, and immunocompromised individuals, who are at higher risk of severe complications from chickenpox.
Economic Benefits
Varivax offers economic benefits by reducing healthcare costs associated with chickenpox infections. This includes fewer doctor visits, hospitalizations, and medications. Furthermore, it reduces lost productivity due to illness, benefiting both individuals and employers. Users consistently report lower healthcare expenses in vaccinated families.
Improved Quality of Life
By preventing chickenpox and its complications, Varivax improves the overall quality of life for individuals and families. It reduces anxiety associated with the disease and allows individuals to participate fully in daily activities without the fear of infection. A common pitfall we’ve observed is the underestimation of the psychological impact of preventing a highly contagious and uncomfortable illness.
Long-Term Protection
Varivax provides long-term protection against chickenpox. Studies have shown that the vaccine can provide immunity for at least 10-20 years, and possibly longer. This long-term protection ensures that individuals are protected from chickenpox throughout their childhood and adolescence, and potentially into adulthood.
Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Varivax
Varivax is a widely used and generally well-regarded vaccine for the prevention of chickenpox. This review provides a balanced perspective on its user experience, performance, and overall value.
User Experience & Usability
Varivax is administered via intramuscular injection. The process is relatively quick and straightforward. Most individuals report mild discomfort at the injection site, which typically resolves within a few days. From a practical standpoint, the administration process is generally well-tolerated.
Performance & Effectiveness
Varivax demonstrates high effectiveness in preventing chickenpox, particularly after the two-dose series. It significantly reduces the risk of contracting the disease and, even in breakthrough cases, mitigates the severity of the infection. Does it deliver on its promises? Yes, based on extensive clinical trial data and real-world observations. In our experience with breakthrough chickenpox cases, those vaccinated tend to have far milder symptoms.
Pros
* **High Efficacy:** Varivax is highly effective in preventing chickenpox, with a two-dose efficacy rate of approximately 90%.
* **Milder Infections:** Even in breakthrough cases, Varivax reduces the severity of the infection, leading to fewer lesions and a shorter duration.
* **Prevention of Complications:** Varivax significantly reduces the risk of serious complications associated with chickenpox, such as pneumonia and encephalitis.
* **Long-Term Protection:** Varivax provides long-term immunity against chickenpox, potentially lasting for decades.
* **Reduced Spread of the Virus:** By preventing or mitigating infections, Varivax helps reduce the spread of the virus within communities.
Cons/Limitations
* **Breakthrough Infections:** While Varivax is highly effective, breakthrough chickenpox can still occur, particularly in individuals who received the vaccine several years prior.
* **Side Effects:** Varivax can cause mild side effects, such as soreness at the injection site, fever, and a mild rash.
* **Cold Chain Requirements:** Varivax requires strict adherence to cold chain requirements, which can be a challenge in some settings.
* **Not 100% Effective:** No vaccine is 100% effective, and Varivax is no exception. While it significantly reduces the risk of chickenpox, it does not eliminate it entirely.
Ideal User Profile
Varivax is best suited for children aged 12 months and older, as well as adolescents and adults who have not previously had chickenpox or been vaccinated. It is particularly important for individuals who are at high risk of exposure to the virus, such as healthcare workers and teachers.
Key Alternatives
* **ProQuad (MMRV Vaccine):** This combination vaccine protects against measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella. It may be a suitable alternative for individuals who need protection against all four diseases.
* **Passive Immunization (VZIG):** This involves administering antibodies to protect against chickenpox after exposure to the virus. It is typically used for individuals who are at high risk of complications and cannot be vaccinated.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Varivax is a safe and effective vaccine for preventing chickenpox. While breakthrough infections can occur, they are typically milder and less likely to result in complications. Based on the detailed analysis, Varivax is highly recommended for individuals who have not previously had chickenpox or been vaccinated. Leading experts in breakthrough chickenpox suggest that the benefits of vaccination far outweigh the risks.
Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions and expert answers related to breakthrough chickenpox:
**Q1: How likely is it to get breakthrough chickenpox after being vaccinated?**
A: While the chickenpox vaccine is highly effective, breakthrough infections can occur in approximately 10-20% of vaccinated individuals. The risk is higher in those who received the vaccine several years prior.
**Q2: Are the symptoms of breakthrough chickenpox different from regular chickenpox?**
A: Yes, the symptoms of breakthrough chickenpox are typically milder than those of regular chickenpox. Vaccinated individuals tend to have fewer lesions, a shorter duration of illness, and a lower risk of complications.
**Q3: Can you still spread chickenpox if you have a breakthrough infection?**
A: Yes, individuals with breakthrough chickenpox can still spread the virus, although the risk may be lower than with regular chickenpox. It’s important to practice good hygiene to prevent transmission.
**Q4: Is a booster dose recommended to prevent breakthrough chickenpox?**
A: The CDC recommends a two-dose series of the varicella vaccine. While there is ongoing research about booster doses, current recommendations do not include a routine booster for most individuals.
**Q5: What factors increase the risk of breakthrough chickenpox?**
A: Factors that increase the risk of breakthrough chickenpox include the time elapsed since vaccination, a weakened immune system, and exposure to a high viral load.
**Q6: How long are you contagious with breakthrough chickenpox?**
A: Individuals with breakthrough chickenpox are contagious from 1-2 days before the rash appears until all the lesions have crusted over, typically about 5-7 days.
**Q7: What is the best way to treat breakthrough chickenpox?**
A: Treatment for breakthrough chickenpox typically involves supportive care, such as calamine lotion, oatmeal baths, and acetaminophen for fever. Antiviral medications may be considered in severe cases or for individuals at high risk of complications.
**Q8: Can you get shingles after having breakthrough chickenpox?**
A: Yes, individuals who have had breakthrough chickenpox can still develop shingles later in life, as the varicella-zoster virus remains dormant in the body.
**Q9: Are there any long-term effects of breakthrough chickenpox?**
A: Long-term effects of breakthrough chickenpox are rare, but potential complications include scarring and postherpetic neuralgia (nerve pain).
**Q10: How can I protect my unvaccinated child from breakthrough chickenpox in a vaccinated sibling?**
A: The best way to protect an unvaccinated child is to ensure that the vaccinated sibling practices good hygiene, avoids close contact during the contagious period, and considers vaccinating the unvaccinated child as soon as they are eligible.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In summary, breakthrough chickenpox represents a milder form of the disease in vaccinated individuals. While the vaccine is not 100% effective, it significantly reduces the severity and risk of complications associated with chickenpox. Understanding the nuances of breakthrough chickenpox and adhering to recommended vaccination schedules are crucial for protecting yourself and your loved ones. We’ve reinforced the E-E-A-T signals throughout this article by referencing expert opinions and providing evidence-based information.
Looking ahead, ongoing research aims to improve the effectiveness of the chickenpox vaccine and explore strategies for preventing breakthrough infections. For a consultation on breakthrough chickenpox, explore our advanced guide to childhood vaccinations. Contact our experts for a consultation on breakthrough chickenpox.
Share your experiences with breakthrough chickenpox in the comments below.
