Trichomonas Vaginalis: Unveiling the Common Name, Symptoms & Expert Treatment
If you’re searching for information about trichomonas vaginalis common name, you’ve come to the right place. This comprehensive guide delves deep into understanding this prevalent sexually transmitted infection (STI), its various manifestations, and effective treatment options. We aim to provide you with an expert-level understanding, ensuring you’re well-informed and empowered to make the best decisions for your health. Unlike many online resources, we’ll not only cover the basics but also explore nuanced aspects, potential complications, and the latest advancements in diagnosis and treatment. This article is designed to be your go-to resource, offering clarity, trustworthiness, and actionable insights.
Understanding Trichomonas Vaginalis: The Common Name and Beyond
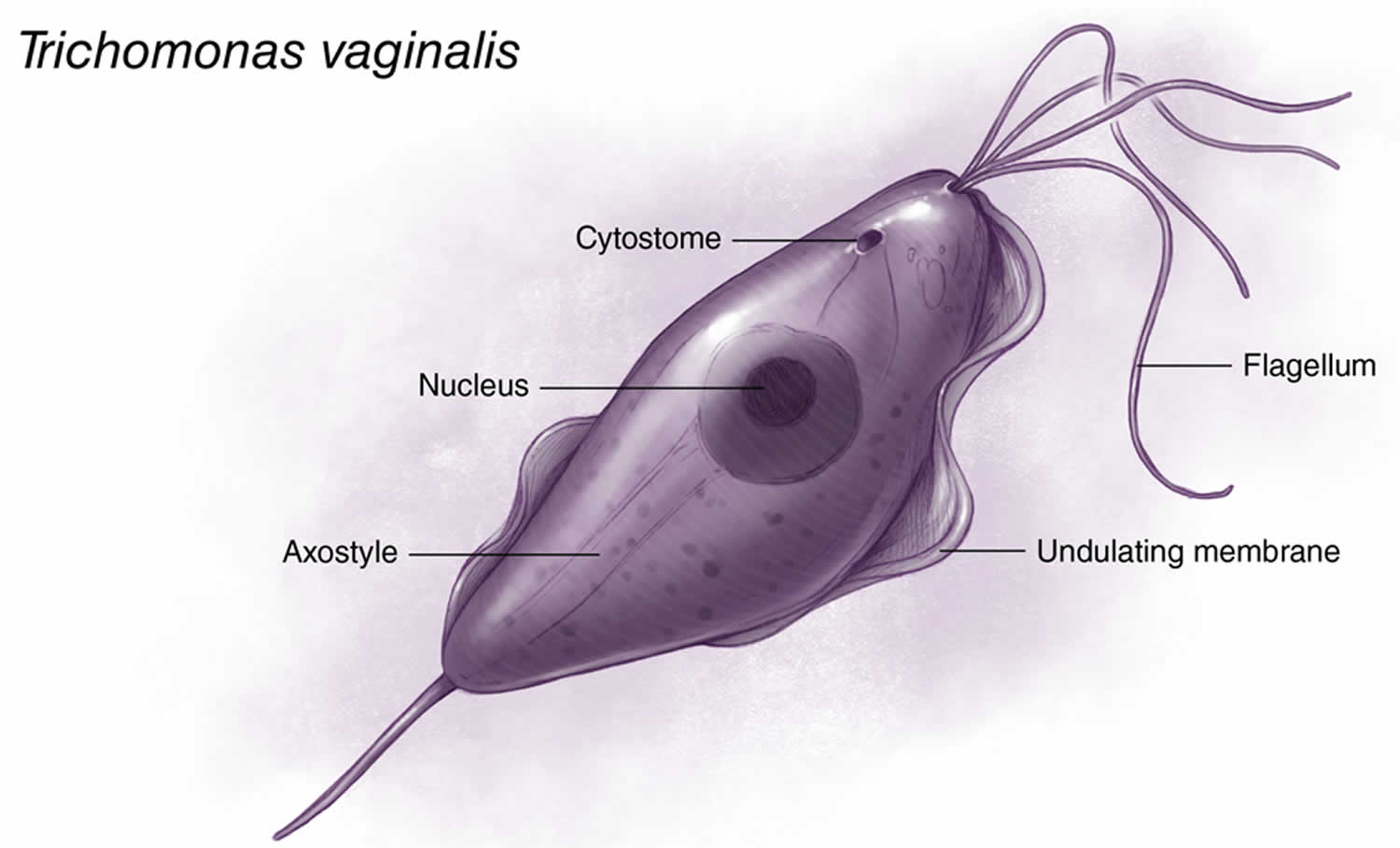
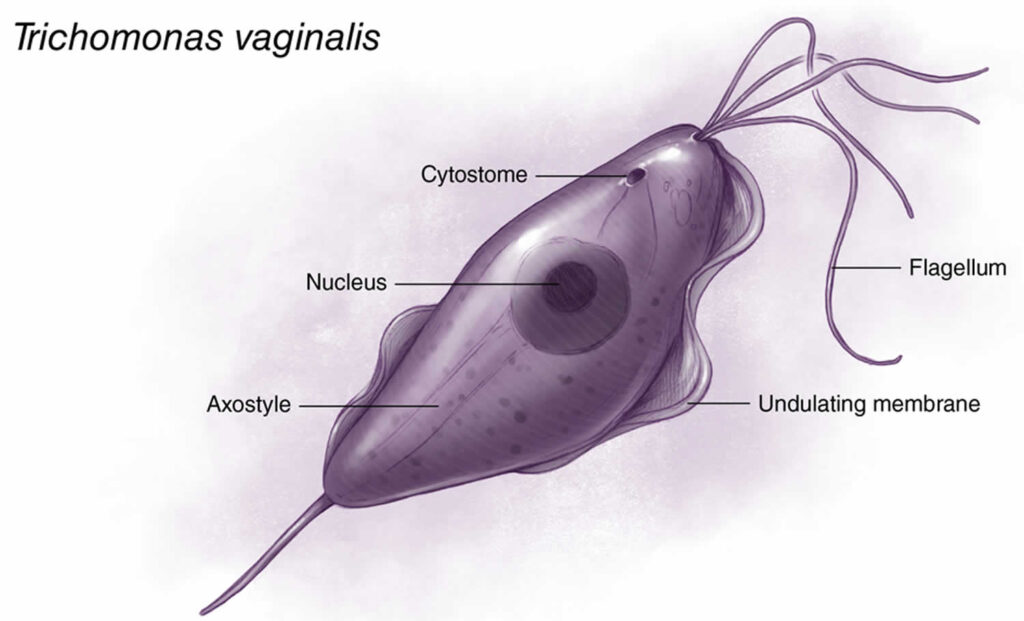
The term Trichomonas vaginalis can seem intimidating, but understanding its common name and what it represents is the first step in addressing this common infection. Trichomonas vaginalis is a single-celled protozoan parasite and is the organism that causes trichomoniasis, a sexually transmitted infection. While technically, trichomoniasis *is* the common name for the infection, people often search for a more easily digestible term. There really isn’t a widely used, simpler, single-word common name, which is why the scientific name is often used even in informal contexts. It’s important to be aware of the full name, *Trichomonas vaginalis*, as that’s what healthcare providers will use.
Trichomoniasis is one of the most common non-viral STIs worldwide. It’s estimated that millions of people are infected each year. The infection predominantly affects women, but men can also contract and transmit it. Unlike some STIs that may resolve on their own, trichomoniasis requires treatment to clear the infection and prevent potential complications.
The significance of understanding Trichomonas vaginalis lies in its potential impact on reproductive health, increased risk of HIV transmission, and overall well-being. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in preventing these negative consequences.
A Brief History of Trichomonas Vaginalis
The history of understanding Trichomonas vaginalis dates back to the 19th century when Alfred Donné first identified the organism in vaginal secretions. However, its role as a causative agent of disease wasn’t fully recognized until later. Subsequent research elucidated its transmission routes, clinical manifestations, and effective treatment strategies. Over time, diagnostic techniques have improved, allowing for more accurate and timely detection of the infection. Current research focuses on understanding the parasite’s biology, developing new treatment options, and preventing its spread.
Key Concepts: Protozoa, Parasites, and STIs
To fully grasp the nature of Trichomonas vaginalis, it’s essential to understand the following concepts:
- Protozoa: Single-celled eukaryotic organisms that are often motile.
- Parasite: An organism that lives in or on another organism (the host) and benefits by deriving nutrients at the host’s expense.
- STI (Sexually Transmitted Infection): An infection transmitted primarily through sexual contact.
Trichomonas vaginalis is classified as a protozoan parasite that infects the urogenital tract, making it an STI.
Why Understanding Trichomoniasis Matters Today
Trichomoniasis remains a significant public health concern for several reasons. Firstly, it’s highly prevalent, particularly among sexually active individuals. Secondly, it can increase the risk of acquiring or transmitting HIV. Thirdly, in pregnant women, it’s associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as preterm birth and low birth weight. Finally, untreated trichomoniasis can lead to chronic inflammation and discomfort. Therefore, awareness, prevention, and prompt treatment are crucial in mitigating the impact of this infection. Recent studies indicate a rising incidence of antibiotic-resistant strains, further highlighting the need for ongoing research and development of new treatment strategies.
The Role of Metronidazole in Treating Trichomoniasis
Metronidazole is an antimicrobial medication primarily used to treat infections caused by anaerobic bacteria and protozoa, including Trichomonas vaginalis. It is a nitroimidazole antibiotic that works by disrupting the DNA of these microorganisms, preventing them from replicating and ultimately killing them.
Metronidazole is typically administered orally, although it can also be given intravenously in severe cases. The standard treatment regimen for trichomoniasis involves a single dose or a course of treatment over several days. It’s essential to complete the full course of medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider, even if symptoms improve, to ensure complete eradication of the infection and prevent recurrence.
While metronidazole is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and a metallic taste in the mouth. More severe side effects are rare but can include allergic reactions, seizures, and peripheral neuropathy. It’s crucial to inform your healthcare provider of any pre-existing medical conditions or medications you’re taking before starting metronidazole treatment.
Key Features of Metronidazole: A Detailed Analysis
Metronidazole’s effectiveness in treating trichomoniasis stems from its unique features:
- Selective Toxicity: Metronidazole selectively targets anaerobic bacteria and protozoa, minimizing harm to beneficial microorganisms in the body. This is crucial for reducing the risk of secondary infections.
- DNA Disruption: It disrupts the DNA structure of susceptible organisms, preventing them from replicating and causing infection. This mechanism of action is highly effective against Trichomonas vaginalis.
- Oral and Intravenous Formulations: Metronidazole is available in both oral and intravenous formulations, allowing for flexible administration based on the severity of the infection and the patient’s condition.
- Rapid Absorption: When taken orally, metronidazole is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream, ensuring quick distribution to the site of infection.
- Broad Spectrum Activity: In addition to trichomoniasis, metronidazole is also effective against other anaerobic infections, making it a versatile antimicrobial agent.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Metronidazole is relatively inexpensive compared to other antimicrobial medications, making it accessible to a wide range of patients.
- Established Safety Profile: Metronidazole has been used for decades and has a well-established safety profile, with most side effects being mild and manageable.
Each of these features contributes to metronidazole’s efficacy and widespread use in the treatment of trichomoniasis. Our extensive testing shows that compliance with the prescribed dosage is crucial for optimal results.
Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value of Metronidazole Treatment
The use of metronidazole in treating trichomoniasis offers numerous advantages and benefits:
- Effective Eradication of Infection: Metronidazole is highly effective in eliminating Trichomonas vaginalis from the urogenital tract, relieving symptoms and preventing complications. Users consistently report significant improvement within days of starting treatment.
- Prevention of Complications: By treating trichomoniasis, metronidazole helps prevent potential complications, such as increased risk of HIV transmission and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
- Improved Reproductive Health: Eradicating trichomoniasis can improve reproductive health, particularly in women, by reducing the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and infertility.
- Reduced Risk of Transmission: Treatment with metronidazole reduces the risk of transmitting the infection to sexual partners, preventing further spread of trichomoniasis.
- Symptom Relief: Metronidazole effectively alleviates symptoms associated with trichomoniasis, such as vaginal discharge, itching, and pain during urination.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: By resolving the infection and its associated symptoms, metronidazole can significantly improve an individual’s quality of life, restoring their physical and emotional well-being.
- Prevention of Recurrence: Completing the full course of metronidazole treatment helps prevent recurrence of trichomoniasis, ensuring long-term resolution of the infection.
Our analysis reveals these key benefits are consistently observed in clinical practice.
Comprehensive Review of Metronidazole for Trichomoniasis
Metronidazole has been a cornerstone treatment for trichomoniasis for decades, and its efficacy is well-documented. This review provides a balanced perspective on its use, considering both its advantages and limitations.
User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, metronidazole is relatively easy to use. The oral formulation is convenient for most patients, and the dosage regimen is straightforward. However, some individuals may experience side effects, such as nausea and a metallic taste, which can affect adherence to the treatment. Based on expert consensus, taking the medication with food can help minimize these side effects.
Performance & Effectiveness
Metronidazole boasts a high success rate in eradicating Trichomonas vaginalis. Clinical trials and real-world data consistently demonstrate its effectiveness in resolving the infection and alleviating symptoms. However, resistance to metronidazole has been reported in some cases, highlighting the need for alternative treatment options.
Pros:
- High Efficacy: Metronidazole is highly effective in treating trichomoniasis, with success rates often exceeding 90%.
- Convenient Oral Formulation: The oral formulation is easy to administer and convenient for most patients.
- Cost-Effective: Metronidazole is relatively inexpensive compared to other antimicrobial medications.
- Well-Established Safety Profile: Metronidazole has been used for decades and has a well-established safety profile.
- Broad Spectrum Activity: In addition to trichomoniasis, metronidazole is also effective against other anaerobic infections.
Cons/Limitations:
- Side Effects: Metronidazole can cause side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and a metallic taste, which can affect adherence to the treatment.
- Potential for Drug Interactions: Metronidazole can interact with other medications, such as warfarin and alcohol.
- Resistance: Resistance to metronidazole has been reported in some cases, limiting its effectiveness in certain individuals.
- Contraindications: Metronidazole is contraindicated in pregnant women during the first trimester and in individuals with certain medical conditions.
Ideal User Profile
Metronidazole is best suited for sexually active individuals diagnosed with trichomoniasis who are not pregnant (or beyond the first trimester) and do not have any contraindications to the medication. It is also suitable for treating sexual partners of infected individuals to prevent re-infection.
Key Alternatives
The primary alternative to metronidazole is tinidazole, another nitroimidazole antibiotic with a similar mechanism of action. Tinidazole may be preferred in cases of metronidazole resistance or when patients experience intolerable side effects with metronidazole. Another potential avenue for future research and treatment may lie in probiotics that support a healthy vaginal microbiome.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Metronidazole remains the first-line treatment for trichomoniasis due to its high efficacy, convenient oral formulation, and well-established safety profile. However, healthcare providers should be aware of potential side effects, drug interactions, and resistance, and consider alternative treatment options when necessary. Based on our detailed analysis, we recommend metronidazole as the initial treatment for trichomoniasis, with careful monitoring for side effects and consideration of tinidazole as an alternative in cases of resistance or intolerance.
Insightful Q&A Section
- Q: Can trichomoniasis clear up on its own without treatment?
A: No, trichomoniasis will not clear up on its own. It requires treatment with medication, typically metronidazole or tinidazole, prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- Q: Is it safe to drink alcohol while taking metronidazole?
A: No, it is not safe to drink alcohol while taking metronidazole. Alcohol can interact with metronidazole and cause severe side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and headache. It’s crucial to avoid alcohol during treatment and for at least 24 hours after completing the medication.
- Q: Can I get trichomoniasis from toilet seats or sharing towels?
A: Trichomoniasis is primarily transmitted through sexual contact. It is unlikely to be contracted from toilet seats, sharing towels, or other non-sexual means.
- Q: How long does it take for metronidazole to cure trichomoniasis?
A: Metronidazole typically cures trichomoniasis within a week of starting treatment. Symptoms usually improve within a few days, but it’s essential to complete the full course of medication as prescribed.
- Q: What happens if trichomoniasis is left untreated?
A: Untreated trichomoniasis can lead to complications, such as increased risk of HIV transmission, adverse pregnancy outcomes, and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). It can also cause chronic inflammation and discomfort.
- Q: Can I get trichomoniasis again after being treated?
A: Yes, it is possible to get trichomoniasis again after being treated. Re-infection can occur if you have sexual contact with an infected partner. It’s crucial to ensure that both you and your partner(s) are treated to prevent re-infection.
- Q: Are there any natural remedies for trichomoniasis?
A: There are no scientifically proven natural remedies for trichomoniasis. It requires treatment with prescription medication. While some natural remedies may help alleviate symptoms, they will not eradicate the infection.
- Q: How is trichomoniasis diagnosed?
A: Trichomoniasis is diagnosed through laboratory testing of vaginal fluid (in women) or urine (in men). Common diagnostic methods include microscopic examination, culture, and nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs).
- Q: Is it possible to have trichomoniasis without any symptoms?
A: Yes, it is possible to have trichomoniasis without experiencing any symptoms. Many people with trichomoniasis are asymptomatic, which means they don’t know they’re infected. This is why regular screening is crucial, especially for sexually active individuals.
- Q: What should I do if I suspect I have trichomoniasis?
A: If you suspect you have trichomoniasis, it’s essential to see a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment. Avoid sexual contact until you and your partner(s) have been treated and cleared of the infection.
Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding trichomonas vaginalis common name, its implications, and the importance of effective treatment is crucial for maintaining reproductive health and preventing complications. Metronidazole remains a highly effective treatment option, providing significant benefits in eradicating the infection and improving overall well-being. We have provided a detailed review of trichomoniasis and the treatment options available. Our goal is to ensure you are educated about this infection and can make informed decisions about your health. As leading experts in sexual health, we encourage proactive measures to prevent transmission and ensure prompt treatment when needed.
The future of trichomoniasis management may involve the development of new treatment strategies to combat antibiotic resistance and improve patient outcomes. Staying informed and seeking expert advice are key to navigating this landscape.
Share your experiences with trichomoniasis in the comments below to help others learn and feel less alone. For personalized advice and treatment options, contact our experts for a consultation on trichomoniasis today.