Uses of Microwaves: A Comprehensive Guide
Microwaves are a ubiquitous part of modern life, found in almost every household and many commercial settings. But beyond simply reheating leftovers, the uses of microwaves extend far beyond what most people realize. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse applications of microwave technology, exploring its fundamental principles, practical applications, and future potential. We aim to provide a definitive resource that not only informs but also showcases the transformative power of microwaves across various industries and daily life.
This article will explore the many uses of microwaves. From cooking and heating to scientific research and medical treatments, we will cover a range of applications, highlighting the technology’s versatility and importance. We will also discuss the underlying science, safety considerations, and future trends in microwave technology, providing a complete overview for anyone interested in learning more about this essential tool.
Understanding Microwaves: The Basics
At their core, microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation, specifically radio waves with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter, and frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. These waves interact with certain molecules, most notably water, fat, and sugar, causing them to vibrate rapidly. This vibration generates heat, which is how microwave ovens cook or reheat food.
The Science Behind Microwave Heating
The process of microwave heating relies on the principle of dielectric heating. When microwaves penetrate a substance containing polar molecules (like water), these molecules attempt to align themselves with the oscillating electromagnetic field. This constant reorientation causes intermolecular friction, which generates heat. The efficiency of this process depends on the frequency of the microwaves and the dielectric properties of the material being heated.
Beyond the Oven: The Broader Spectrum of Microwave Applications
While the domestic microwave oven is the most familiar application, the uses of microwaves extend far beyond the kitchen. In industrial settings, microwaves are used for drying materials, sterilizing equipment, and even processing rubber. In telecommunications, microwaves are essential for transmitting signals over long distances. In medicine, they are used in various diagnostic and therapeutic applications. This broad range of applications highlights the versatility and importance of microwave technology.
Microwaves in the Kitchen: A Culinary Revolution
The most common application of microwaves is, without a doubt, cooking and reheating food. Microwave ovens have revolutionized the way we prepare meals, offering speed and convenience that traditional ovens cannot match. From quick snacks to complete meals, microwaves have become an indispensable kitchen appliance.
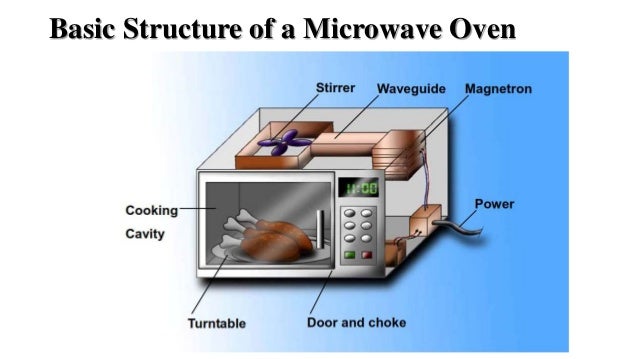
The Microwave Oven: A Detailed Look
A typical microwave oven consists of a magnetron, which generates microwaves; a waveguide, which directs the microwaves into the cooking chamber; a turntable, which ensures even heating; and a control panel, which allows users to set the cooking time and power level. The microwaves bounce around the interior of the oven, penetrating the food from all angles and heating it quickly and efficiently.
Beyond Reheating: Creative Microwave Cooking
While reheating leftovers is a common use, microwaves can also be used for more sophisticated cooking tasks. Steaming vegetables, poaching eggs, and even baking cakes are all possible in a microwave oven. With the right techniques and recipes, microwaves can be a versatile tool for creating delicious and nutritious meals. Many modern microwave ovens come with pre-set programs for various food types, making cooking even easier and more convenient.
Industrial Uses of Microwaves: Efficiency and Precision
Beyond the kitchen, microwaves play a crucial role in various industrial processes. Their ability to generate heat quickly and efficiently makes them ideal for applications such as drying, sterilization, and material processing. In many cases, microwave technology offers advantages over traditional methods in terms of speed, energy efficiency, and precision.
Microwave Drying: Speeding Up Production
Microwave drying is used in industries such as food processing, textiles, and pharmaceuticals. The microwaves penetrate the material, heating it from the inside out and evaporating moisture quickly and evenly. This method is faster and more energy-efficient than traditional drying methods, which rely on heating the surface of the material and waiting for the moisture to evaporate.
Microwave Sterilization: Ensuring Safety
Microwave sterilization is used to kill microorganisms in medical equipment, food products, and other materials. The microwaves generate heat that destroys the cells of bacteria, viruses, and fungi. This method is faster and more effective than traditional sterilization methods, such as autoclaving, and it can be used to sterilize heat-sensitive materials without damaging them.
Microwave Material Processing: Tailoring Properties
Microwaves are used in material processing to modify the properties of various materials, such as rubber, plastics, and ceramics. The microwaves can selectively heat certain components of the material, causing them to react or transform in a controlled manner. This allows manufacturers to tailor the properties of the material to meet specific requirements, such as strength, flexibility, or conductivity.
Microwaves in Telecommunications: Connecting the World
Microwaves are essential for transmitting signals over long distances in telecommunications. They are used in satellite communications, cellular networks, and radar systems. The high frequency of microwaves allows them to carry large amounts of data, making them ideal for transmitting voice, video, and other types of information.
Satellite Communications: Reaching Remote Areas
Satellites use microwaves to transmit signals to and from ground stations. The microwaves are beamed up to the satellite, which amplifies the signal and retransmits it to another ground station. This allows communication with remote areas that are not easily accessible by other means.
Cellular Networks: Enabling Mobile Communication
Cellular networks use microwaves to transmit signals between cell towers and mobile devices. The microwaves are transmitted over short distances, allowing users to communicate wirelessly while on the move. The increasing demand for mobile data has led to the development of more advanced microwave technologies, such as millimeter-wave communication, which can transmit even larger amounts of data.
Radar Systems: Detecting Objects
Radar systems use microwaves to detect objects, such as airplanes, ships, and weather patterns. The radar emits microwaves, which bounce off the object and return to the radar receiver. By analyzing the reflected microwaves, the radar can determine the object’s distance, speed, and direction.
Microwaves in Medicine: Diagnosis and Therapy
Microwaves are used in various diagnostic and therapeutic applications in medicine. They can be used to image internal organs, heat tumors, and even deliver drugs directly to cancer cells. The precision and non-invasive nature of microwave technology make it an attractive option for many medical procedures.
Microwave Imaging: Seeing Inside the Body
Microwave imaging is a non-invasive technique that uses microwaves to create images of internal organs. The microwaves are transmitted through the body, and the reflected waves are analyzed to create an image. This technique can be used to detect tumors, diagnose diseases, and monitor the effectiveness of treatments.
Microwave Hyperthermia: Treating Cancer
Microwave hyperthermia is a technique that uses microwaves to heat tumors, killing cancer cells. The microwaves are focused on the tumor, raising its temperature to a level that is lethal to cancer cells but not harmful to healthy tissue. This technique can be used in conjunction with other cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Microwave Drug Delivery: Targeting Cancer Cells
Microwaves can be used to deliver drugs directly to cancer cells. The drugs are encapsulated in nanoparticles that are designed to absorb microwaves. When the nanoparticles are exposed to microwaves, they heat up and release the drugs, killing the cancer cells. This technique can be used to target cancer cells more effectively than traditional drug delivery methods, reducing side effects and improving treatment outcomes.
The Future of Microwaves: Innovation and Potential
The uses of microwaves are constantly evolving as researchers and engineers develop new applications and improve existing technologies. From advanced cooking appliances to cutting-edge medical treatments, the future of microwaves is full of exciting possibilities. As technology advances, we can expect to see even more innovative uses of microwaves in the years to come.
Advanced Cooking Appliances: Smart and Efficient
Future microwave ovens may incorporate advanced features such as sensors that detect the type and quantity of food being cooked, automatically adjusting the cooking time and power level. They may also be connected to the internet, allowing users to download recipes and control the oven remotely. These smart appliances will make cooking even easier and more convenient.
New Medical Treatments: Precise and Non-Invasive
Researchers are exploring new ways to use microwaves in medicine, such as for treating neurological disorders and delivering gene therapy. These treatments will be more precise and less invasive than traditional methods, reducing side effects and improving patient outcomes. The potential for microwaves to revolutionize medical care is immense.
Industrial Innovations: Sustainable and Efficient
In industry, microwaves are being used to develop more sustainable and efficient processes. For example, they can be used to recycle materials, treat wastewater, and produce biofuels. These innovations will help reduce waste, conserve resources, and mitigate climate change. The role of microwaves in creating a more sustainable future is increasingly important.
Safety Considerations When Using Microwaves
While microwaves offer numerous benefits, it’s important to use them safely. Understanding the potential risks and following safety guidelines can help prevent accidents and ensure that microwaves are used responsibly.
Potential Risks: Radiation and Burns
One of the main concerns about microwaves is the potential for radiation exposure. However, microwave ovens are designed to contain the microwaves inside the cooking chamber. As long as the oven is in good working condition and the door is properly sealed, there is no risk of harmful radiation exposure. Burns are another potential risk, especially when heating liquids or foods that can splatter. Always use caution when removing hot items from the microwave and allow them to cool slightly before handling.
Safety Guidelines: Best Practices
To ensure safe microwave use, follow these guidelines:
- Never use a microwave oven with a damaged door or seal.
- Use microwave-safe containers and utensils.
- Avoid heating liquids in sealed containers, as they can explode.
- Stir food during cooking to ensure even heating.
- Allow food to cool slightly before handling.
- Clean the microwave oven regularly to prevent food buildup.
Uses of Microwaves: Q&A
Here are some frequently asked questions about the uses of microwaves:
- Question: Can microwaves cause cancer?
- Answer: No, microwaves do not cause cancer. They are a form of non-ionizing radiation, which means they do not have enough energy to damage DNA.
- Question: Are microwave ovens safe to use?
- Answer: Yes, microwave ovens are safe to use as long as they are in good working condition and used according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Question: Can I use metal in the microwave?
- Answer: No, you should not use metal in the microwave. Metal can cause sparks and damage the oven.
- Question: How do microwaves heat food?
- Answer: Microwaves heat food by causing water molecules to vibrate, which generates heat.
- Question: What are some common uses of microwaves besides cooking?
- Answer: Microwaves are used in telecommunications, medicine, and industry for various applications such as drying, sterilization, and imaging.
- Question: Can microwaves kill bacteria in food?
- Answer: Yes, microwaves can kill bacteria in food if the food is heated to a high enough temperature.
- Question: How can I ensure even heating in the microwave?
- Answer: To ensure even heating, stir food during cooking and use a turntable if your microwave has one.
- Question: What types of containers are safe to use in the microwave?
- Answer: Microwave-safe glass, plastic, and ceramic containers are safe to use in the microwave.
- Question: What is microwave hyperthermia?
- Answer: Microwave hyperthermia is a technique that uses microwaves to heat tumors, killing cancer cells.
- Question: Are there any environmental concerns associated with microwaves?
- Answer: While microwaves themselves do not directly contribute to environmental issues, the energy consumption of microwave ovens can have an impact. Using energy-efficient models and minimizing unnecessary use can help reduce their environmental footprint.
Conclusion
The uses of microwaves are vast and varied, extending far beyond the familiar kitchen appliance. From industrial processes to medical treatments and telecommunications, microwaves play a crucial role in modern life. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of microwave technology in the future. Whether it’s improving the efficiency of industrial processes or developing new medical treatments, the potential for microwaves to transform our world is immense. We encourage you to share your experiences with microwaves in the comments below and explore our advanced guides to related topics to further your understanding of this fascinating technology.
